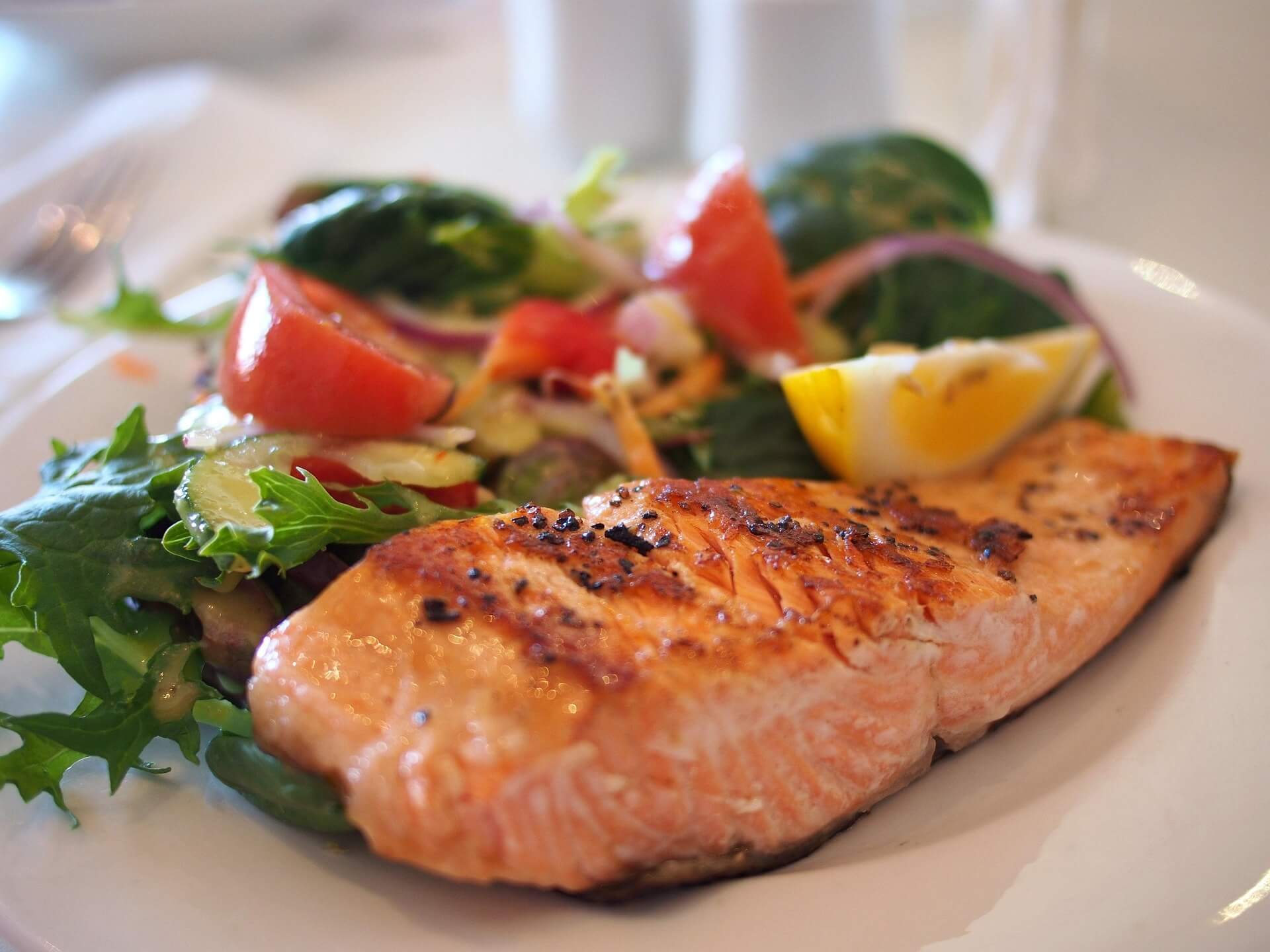To effectively manage diabetes, a well-balanced diet is required, which helps regulate blood sugar levels while also supplying necessary nutrients for overall health. The appropriate foods can help minimize blood sugar increases, lower the risk of problems, and increase energy levels. The following are the top 10 diabetes-friendly foods that are extremely useful to people with diabetes.
Table of Contents
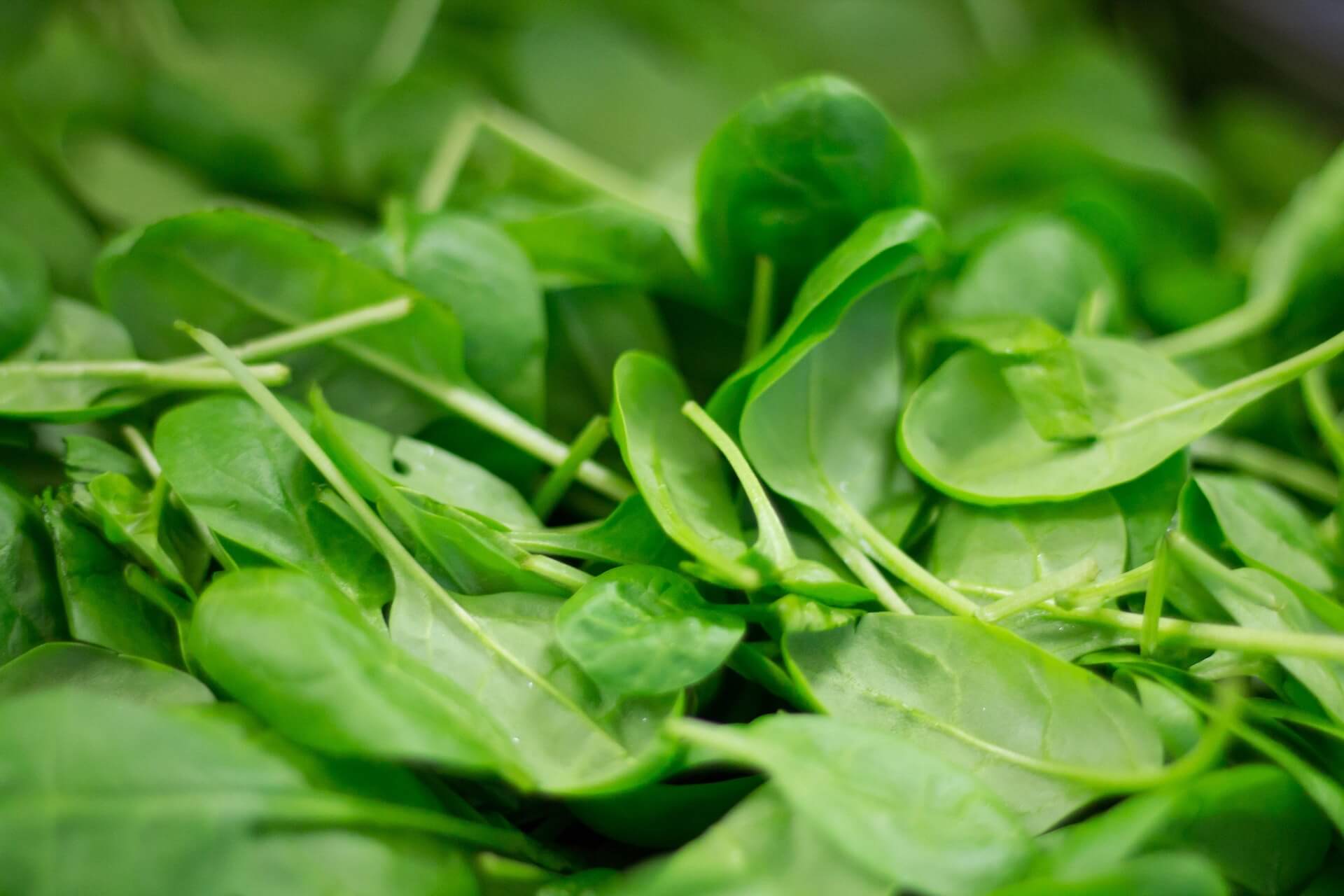
1. Leafy Green Vegetables
Examples: Spinach, Swiss Chard, Collard Greens, Kale
Leafy greens are low in calories and carbs, but high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are especially high in vitamin C, which has been demonstrated to reduce inflammation and improve blood sugar control in people with type 2 diabetes.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- Almost no influence on blood sugar.
- High in antioxidants that promote eye and heart health.
- Excellent supply of magnesium, which improves insulin sensitivity.
Check out Why Leafy Green Vegetables Are Essential for Those with Diabetes.
2. Fatty Fish
Examples: Tuna, Salmon, Sardines, Mackerel
Fatty fish are high in omega-3 fatty acids (EPA and DHA), which are essential for lowering inflammation, maintaining heart health, and boosting insulin sensitivity.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- Reduces risk of heart disease, a significant diabetic consequence.
- Improves brain function and decreases inflammation.
- Provides high-quality protein, keeping you satisfied for longer.
3. Whole Grains
Examples: Brown Rice, Whole Oats, Barley, Quinoa
Whole grains, unlike refined grains, have more fiber and minerals, slowing the digestion process and resulting in moderate blood sugar increases rather than spikes.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- High fiber content helps manage blood glucose levels.
- Reduces insulin resistance.
- Promotes gut health by feeding beneficial bacteria.
4. Beans and Legumes
Examples: Kidney Beans, Black Beans, Lentils, Chickpeas
Beans and legumes are nutrient-dense foods high in protein, fiber, and slow-digesting carbs, making them a good choice for diabetics.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- Low glycemic index helps to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- High fiber content promotes intestinal health.
- Packed with magnesium and potassium, which promote heart health.
5. Nuts and Seeds
Examples: Almonds, Walnuts, Flaxseeds, Chia Seeds
Nuts and seeds are high in healthy fats, fiber, and protein, making them a great snack that does not produce significant blood sugar rises.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- Reduces insulin resistance.
- Provides beneficial fats that reduce harmful cholesterol.
- Chia and flaxseeds provide omega-3s and fiber, which help manage blood sugar.
6. Berries
Examples: Strawberries, Blueberries, Raspberries, Blackberries
Berries are low in sugar but abundant in antioxidants and fiber, making them an excellent fruit choice for diabetics.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- Packed in antioxidants that prevent inflammation.
- High fiber content reduces glucose absorption.
- Promotes brain and heart health.
7. Greek Yogurt
Greek yogurt is a protein-rich, low-carb dairy product that can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Why It’s Good for Diabetes:
- Probiotics promote intestinal health.
- High protein content, which helps suppress appetite.
- Lower in carbs than ordinary yogurt.
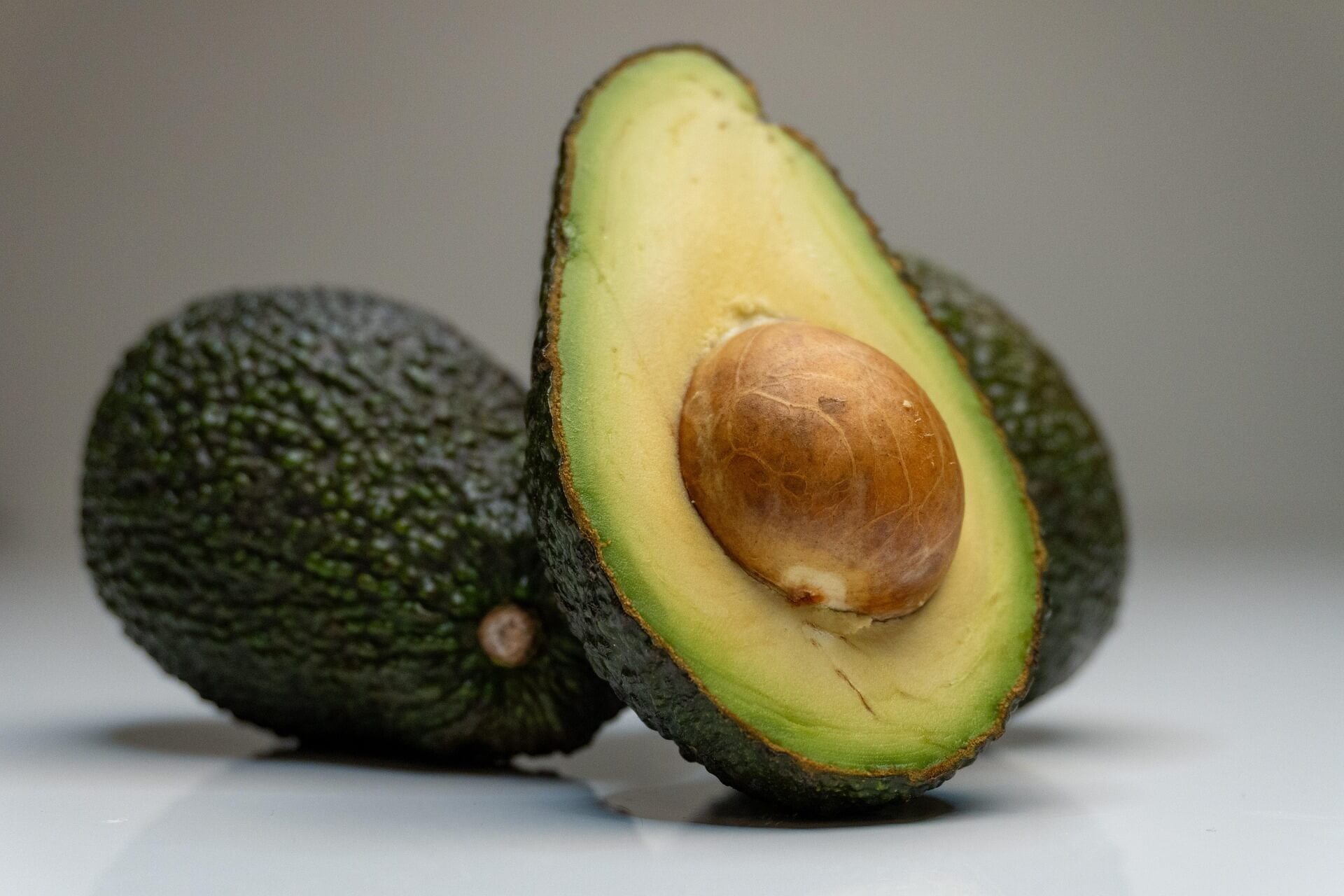
8. Avocados
Avocados are high in healthy monounsaturated fats, fiber, and vitamins.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- Improves insulin sensitivity.
- Improves heart health by lowering harmful cholesterol.
- High fiber content stabilizes blood sugar levels.
Get more details on Why People with Diabetes Should Eat Avocados.
9. Eggs
Eggs are high in protein and include vital minerals such as choline and lutein.
Why They’re Good for Diabetes:
- Helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Increases satiety, decreasing the need for unhealthy snacking.
- Contains antioxidants that promote eye health.
10. Cinnamon
Though not a “food” in high quantities, cinnamon is a spice that can decrease blood sugar and enhance insulin sensitivity.
Why It’s Good for Diabetes:
- Reduces fasting blood glucose levels.
- Reduces insulin resistance.
- Contains anti-inflammatory properties.
Top 10 Diabetes-Friendly Foods Conclusion
Including these top ten items in your diet will help you manage diabetes by stabilizing blood sugar, boosting insulin sensitivity, and lowering inflammation. However, quantity control and balanced eating habits are also important. Before making any big dietary changes, always speak with a healthcare expert or a nutritionist.